在上一篇介紹完了如何讓ViewModel和Entity之間的轉換透過AutoMapper變的更簡單,然後透過框架讓設定ViewModel和Entity之間的對應關係變的容易。
在這一篇,將會看Data Access Layer (DAL)的部份,也就是儲存資料層的部份。
Data Acce Layer (DAL)
不管任何大小的軟體,通常都會需要儲存資料。而這個儲存資料最常見的就是儲存到資料庫裡面。以Asp .Net Mvc來說,最常見的就是透過Entity Framework這個ORM的技術來儲存到實體的資料庫,例如MS Sql,Oracle等。
而如果以Entity Framework來講,它所在的角色就屬於DAL層。
以一般比較常見的三層是架構,大概就會如下圖:
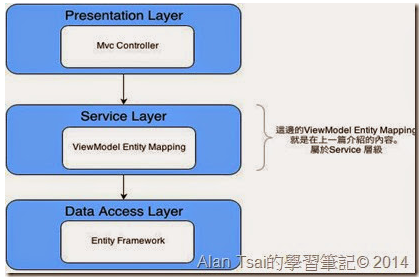
一般的三層式架構 – 裡面白色的表示Mvc裡面比和3層式架構較相近的對應
用Entity Framework做DAL的問題
其實這個問題不只有使用Entity Framework會,任何的DAL實作都有這個問題。
舉個例子來說,假設今天我們用的是Entity Framework作為DAL層,如果開發到一半,對方突然要求不要使用Entity Framework,而是要改成傳統的ADO .Net作為DAL怎麼辦?
或者說如果要做單元測試(Unit Testing),肯定不希望在跑的時候還是連資料庫,而是希望連一些假資料,這時候怎麼辦?
解決方法其實很簡單,就是把實際的DAL在抽一層出來,就有了所謂的Repository Pattern。
Repository Pattern
一般來說,在寫Mvc裡面最長看到的Pattern就是Repository Pattern。
這個Pattern概念非常簡單,Repository其實有儲存庫的意思,所以這個Pattern的意思是,把實際的DAL層透過所謂的Repository封裝之後,從外面的角度來說是和Repository 溝通來取得資料,至於Repository的資料來源是那裡,就不管了。
文字敘述可能有些抽象,我們來看一張圖:
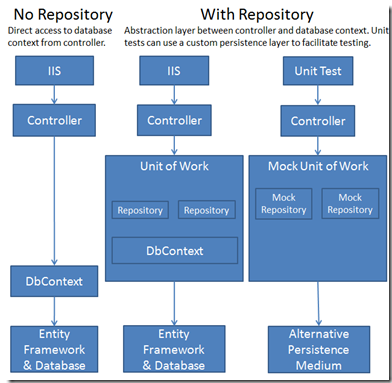
Repository的好處:圖片來源: Implementing the Repository and Unit of Work Patterns in an ASP.NET MVC Application (9 of 10)
可以看到,左邊的圖是一般直接用Entity Framework,而右邊使用了Repository Pattern + Unit of Work(下一篇介紹),因此可以再真實的環境用Entity Framework連資料庫,然後在單元測試的時候,連假資料。
這樣就可以把實際的資料來源抽象化,提供更大的彈性。
定義Repository的interface
Repository有很多種實作方法,共通的來說,1個Repository代表一個DB 裡面的 Table。通常的做法有兩種,一種是每一個Table就一個interface,另外一種是以Generic的方式,寫一種通用型的Repository。
我這邊會介紹的是通用型的Repository。
首先,一般的DB 動作有所謂的CRUD,因此我們的interface就至少會包含這幾種動作。同時,我們還會有一個SaveChanges的方法,代表把目前有記錄的動作執行。
/// <summary>
/// 代表一個Repository的interface。
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">任意model的class</typeparam>
public interface IRepository<T>
{
/// <summary>
/// 新增一筆資料。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity">要新增到的Entity</param>
void Create(T entity);
/// <summary>
/// 取得第一筆符合條件的內容。如果符合條件有多筆,也只取得第一筆。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="predicate">要取得的Where條件。</param>
/// <returns>取得第一筆符合條件的內容。</returns>
T Read(Expression<Func<T, bool>> predicate);
/// <summary>
/// 取得Entity全部筆數的IQueryable。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Entity全部筆數的IQueryable。</returns>
IQueryable<T> Reads();
/// <summary>
/// 更新一筆資料的內容。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity">要更新的內容</param>
void Update(T entity);
/// <summary>
/// 刪除一筆資料內容。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity">要被刪除的Entity。</param>
void Delete(T entity);
/// <summary>
/// 儲存異動。
/// </summary>
void SaveChanges();
}定義好了之後,我們就來看實作。
Entity Framework的Repository interface實作
再來我們就定義一個EF版本的Repository實作:
/// <summary>
/// 實作Entity Framework Generic Repository 的 Class。
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TEntity">EF Model 裡面的Type</typeparam>
public class EFGenericRepository<TEntity> : IRepository<TEntity>
where TEntity : class
{
private DbContext Context { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 建構EF一個Entity的Repository,需傳入此Entity的Context。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="inContext">Entity所在的Context</param>
public EFGenericRepository(DbContext inContext)
{
Context = inContext;
}
/// <summary>
/// 新增一筆資料到資料庫。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity">要新增到資料的庫的Entity</param>
public void Create(TEntity entity)
{
Context.Set<TEntity>().Add(entity);
}
/// <summary>
/// 取得第一筆符合條件的內容。如果符合條件有多筆,也只取得第一筆。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="predicate">要取得的Where條件。</param>
/// <returns>取得第一筆符合條件的內容。</returns>
public TEntity Read(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate)
{
return Context.Set<TEntity>().Where(predicate).FirstOrDefault();
}
/// <summary>
/// 取得Entity全部筆數的IQueryable。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Entity全部筆數的IQueryable。</returns>
public IQueryable<TEntity> Reads()
{
return Context.Set<TEntity>().AsQueryable();
}
/// <summary>
/// 更新一筆Entity內容。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity">要更新的內容</param>
public void Update(TEntity entity)
{
Context.Entry<TEntity>(entity).State = EntityState.Modified;
}
/// <summary>
/// 更新一筆Entity的內容。只更新有指定的Property。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity">要更新的內容。</param>
/// <param name="updateProperties">需要更新的欄位。</param>
public void Update(TEntity entity, Expression<Func<TEntity, object>>[] updateProperties)
{
Context.Configuration.ValidateOnSaveEnabled = false;
Context.Entry<TEntity>(entity).State = EntityState.Unchanged;
if (updateProperties != null)
{
foreach (var property in updateProperties)
{
Context.Entry<TEntity>(entity).Property(property).IsModified = true;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 刪除一筆資料內容。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity">要被刪除的Entity。</param>
public void Delete(TEntity entity)
{
Context.Entry<TEntity>(entity).State = EntityState.Deleted;
}
/// <summary>
/// 儲存異動。
/// </summary>
public void SaveChanges()
{
Context.SaveChanges();
// 因為Update 單一model需要先關掉validation,因此重新打開
if (Context.Configuration.ValidateOnSaveEnabled == false)
{
Context.Configuration.ValidateOnSaveEnabled = true;
}
}
}使用Entity Framework的Repository
基本上,我們也是一樣可以用Autofac做注入,不過因為最終我們會用到Unit of Work,所以這邊我就先不注入,純粹展示使用方法。
下面範例基本上會用註解顯示之前用Entity Framework Context的用法(db是代表context),可以做一個用Repository和用原生EF Context的比較。其實用起來差不多。
注入的部分
首先看一下我們如何注入Repository進來:
public class PostsController : Controller
{
// 預設Scaffolding出來的Entity Context
// private BlogEntities db = new BlogEntities();
private IRepository<Post> repo;
public PostsController()
: this(new EFGenericRepository<Post>(new BlogEntities()))
{
}
public PostsController(IRepository<Post> inRepo)
{
repo = inRepo;
}
....Create和Read(Index)用法比對
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Create(Post post)
{
...
// db.Post.Add(post);
// db.SaveChanges();
repo.Create(post);
repo.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
....
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
//return View(db.Post.ToList());
return View(repo.Reads().ToList());
}
public ActionResult Details(int? id)
{
...
// Post post = db.Post.Find(id);
Post post = repo.Read(x => x.Id == id);
...
}Update和Delete用法比對
...
public ActionResult Edit(EditViewModel post)
{
...
// db.Entry(postEntity).State = EntityState.Modified;
// db.SaveChanges();
repo.Update(postEntity);
repo.SaveChanges();
...
}
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id)
{
...
//db.Post.Remove(post);
//db.SaveChanges();
repo.Delete(post);
repo.SaveChanges();
...
}看過這幾個常見的比對,應該發現和之前(直接使用EF的Context)用法差不多,但是對未來的彈性大幅度提到,下面將舉一個簡單的例子。
模擬要做單元測試,把Repository實作抽換
因為我們的Controller會要的是IRepository,因此當要做單元測試的時候,我們可以給另外一個實作,例如:
public class FakeRepository<Post>
: IRepository<Post>
{
private List<Post> data;
public FakeRepository()
{
data = new List<Post>();
data.Add(new Post()
{
Id = 1,
CreateDateTime = DateTime.Now,
LastModifyDateTime = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-10),
PostContent = "abc",
Title = "123"
});
}
public IQueryable<Post> Reads()
{
return data.AsQueryable();
}
// ...其他方法那做單元測試就簡單並且減少時間(不需要和DB溝通),因為資料是我們灌好的假資料,可以掌控內容。
結語
希望透過這一篇,對於為什麼和如何使用Repository Pattern會有些概念,不過Repository本身還是有些問題。
一個DB肯定不止一個Table,而Repository只代表了一個Table,那如果我同時要用2個Table以上怎麼辦?這個時候Unit of work就進來了。
Unit of work就留到下一篇在講了。
